club foot horse cause
Bandaging can also cause the soft tissue in the affected limb to relax. A foals bones growing too.
What Advice Has Been Most Helpful When You First Encounter A Club Foot
Many stem from the understanding that situations limiting the range of movement in a horses limb can cause a hoof to grow more upright.
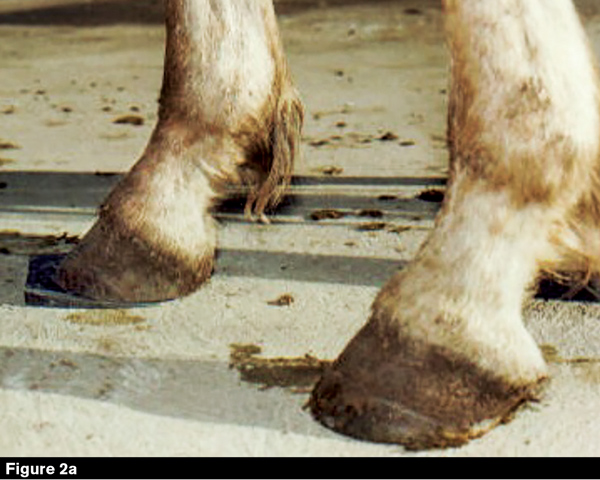
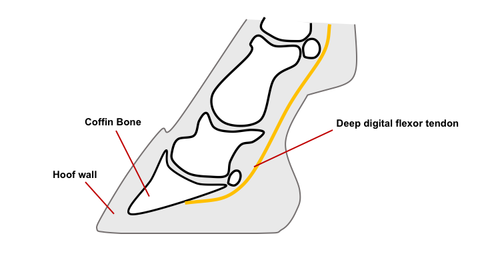
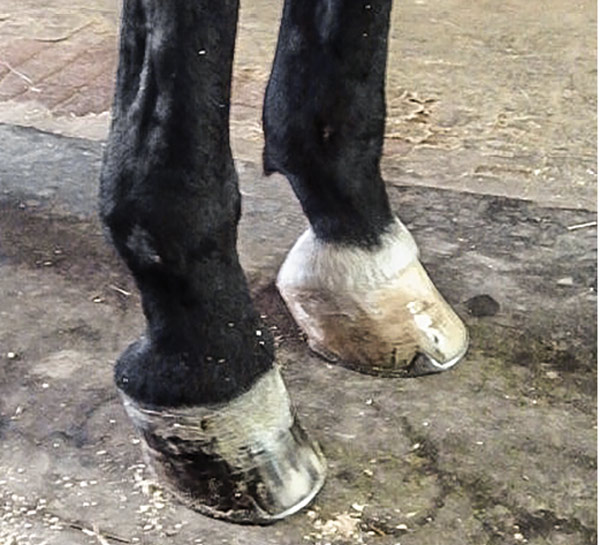
. Example of a club foot. A club foot is an upright foot caused by a shortening of the tendon and muscle of deep digital flexor unit. 4-H Tack Sale Drop-Off.
The affected leg or foot may be slightly shorter. Treatment varies with the age of the horse and. Field Trip to Mid Atlantic Equine Medical Center.
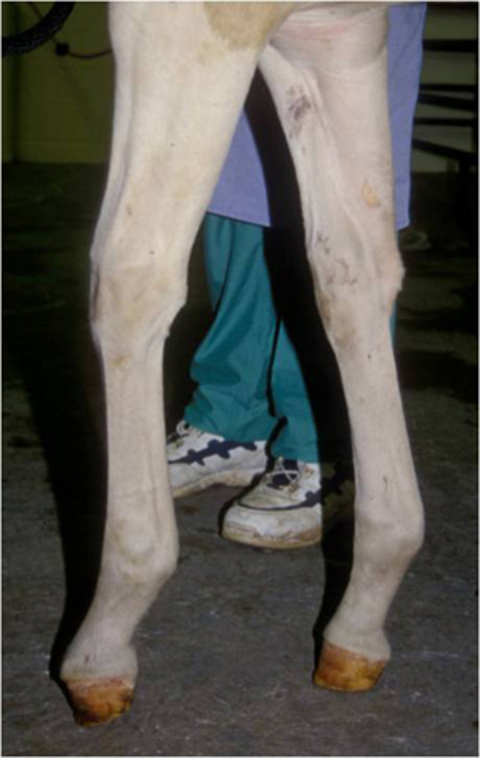
The characteristics of a flexure limb deformity commonly referred to as club foot are easy to identify. Veterinarians tend to classify club feet either by type or by grade. Example of a club foot.
This report contains information on the symptoms causes treatment and prognosis of club foot. Any club foot that has been around a while will have a sensitive unused underdeveloped frogdigital cushion. Poor trimming can be corrected whereas a club foot cannot be corrected.
After more than 50 years of experience as. If the condition persists after weaning surgery will probably be needed. Causes of Club Foot in Horses.
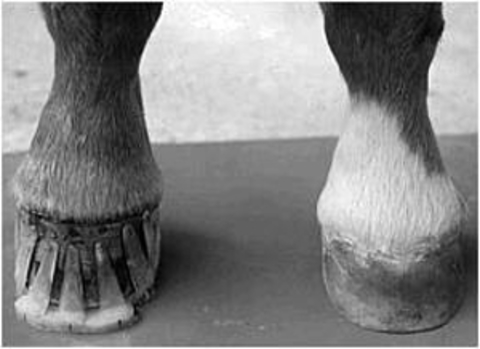
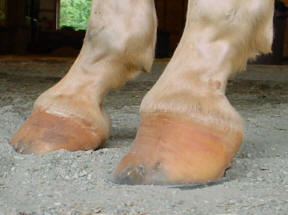
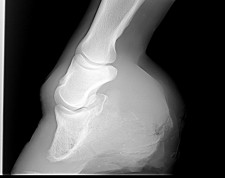
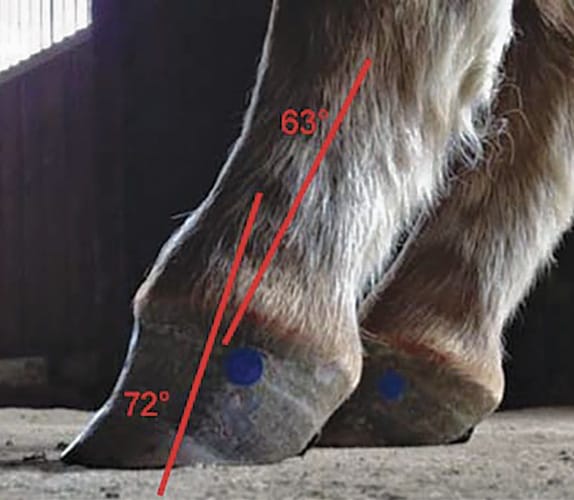
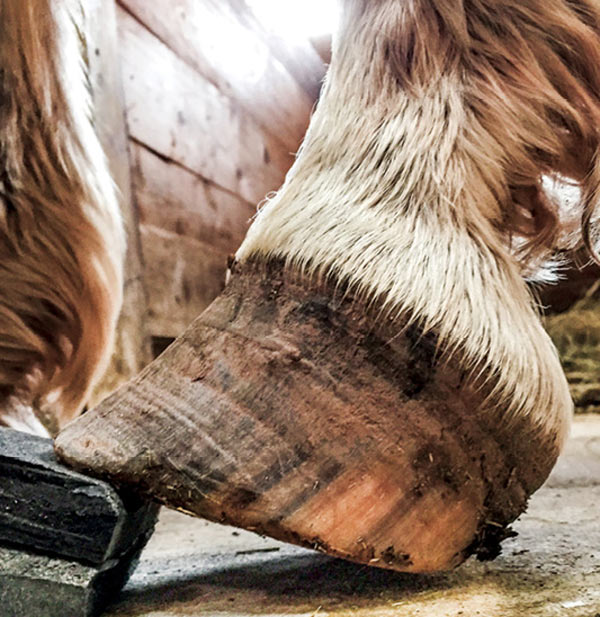
Caused by abnormal contraction of the deep digital flexor tendon a club foot puts pressure on the coffin joint and initiates a change in a hoofs biomechanics. The normal range of hoof angle is 50 to 55 degrees while a club foot might stand at more than 60 degrees. Growth rings are wider at the heel the toe is usually dished the hoof is high on the heel and the coffin joint axis is broken forward.
A diet rich in calories and sugar can cause problems as well. Treatment varies with the age of the horse and. Radiographs often reveal that the coffin bone is deformed or remodeled.
The excessive pull on the deep digital flexor tendon DDFT turns the coffin bone downward loading shifts to the toe area and the hoof changes shape in response. A foals bones growing too. Often club foot affects both front legs with one being more severe than the other.
March 18th 5-9pm 4-H Tack Sale. Animal Protection and Welfare. High heels in a normal hoof are very different from the high heels of a club foot and poor trimming does not result in a club foot.
An injury to the foot is a. The calf muscles in the affected leg are usually underdeveloped. If a horse has a clubbed foot then the foals that mare or stud produces will have one as well.
Generally the greater the upright angle the more severe the club foot. With respect to the club foot the heel of the affected foot grows faster and the hoof. An injury to the foot is a.
The deep flexor tendon is shorter than the bones causing a pulling on the coffin bone in the hoof which causes a deformity in the shape of the hoof. Telltale signs of a club foot may include an excessively steep hoof angle a distended coronary band growth rings that are wider. In the genetic club footed horse the cannon bone of the clubby foot is slightly shorter and so too is the tendon shorter than the normal leg.
There are varying degrees of club foot. It also may cause decreased blood flow to the foot which results in thin soles that are prone to abscesses. Friday March 19th 5 - 9pm Saturday March 20th 9am - 2pm County Presentations.
There are several causes of club foot. If a horse puts more weight on the inside of a hoof the blood is pushed to the opposite side of the foot causing faster growth and wearing down the weighted surface at a faster rate. We continue to learn more about the function and biomechanics of the horses foot and develop new and innovative strategies to alter those biomechanics and mitigate problems that lead to lameness in the foot.
Caused by abnormal contraction of the deep digital flexor tendon a club foot puts pressure on the coffin joint and initiates a change in a hoofs biomechanics. A club foot may also result from injury if the horse is lame and keeps favoring the sore foot not putting much weight on the heel. Type 1 means that the hoof to ground angle at the front of the hoof is greater than 60 degrees but less than or.
Be aware that horses that develop a club foot will always have one foot smaller than the other have a weak toe that may need the protection afforded by a shoe if ridden may have limb length disparity are. Causes of Club Foot in Horses. Congenital deformity at birth occurring within the mares uterus likely due to multiple factors.
The primary one is genetics. Podiatry in equine veterinary practice is gaining increasing attention. The foot may be turned so severely that it actually looks as if its upside down.
Horse Heroes is an animal shelter or animal welfare organization in Piscataway NJ that was founded in 2018. Efficacy and safety of suprachoroidal triamcinolone injection in horses with poorly. 2pm Monday February 15 2010 Horse Bowl.
You can fix everything else and still have the back of the foot too sensitive for the horse to land on which will cause the shortened stride and resulting club foot on its own another vicious cycle. The up foot is accompanied by a broken forward pastern that is the hoof is steeper than the pastern Photo 1. Club foot can occur before or after birth in foals.
March 17th Thurs. This lack of use may cause shortening and contracting of the muscles and tendons in that leg eventually making that foot more upright. The more immobilization applied to a limb the more laxity is achieved to.
Club foot can develop in mature horses too for similar reasonsany injury or chronic pain that causes a horse to consistently favor one foot can lead to contracting and shortening of the muscles and tendons specifically the deep digital flexor tendon and muscle apparatus in that leg eventually pulling the foot into a more upright position. But what causes it. Most recent tax filings.
Causes of club foot Club foot has several possible causes. In the horse hoof growth is dictated in large part by weight distribution. INJURY One of the more commonly accepted causes is the result of an injury most notably supra-scapular nerve damage.
In club footed horses the abnormal contraction of the tendon causes the coffin bone to rotate which pulls the toe down and creates that upright hoof structure. March 25 2010 Horse Registration Forms for State Events Due In. After birth foals acquire club feet when the bones grow faster than the tendons.
Foaling trauma foal grazing stance overly fast growth of limbs injury or. The classic club foot is upright and contracted and there may be a. Club foot refers to a tendon flaw that causes the hoof to be very upright.
Frequently there is mild flexion of the coffin joint with a broken hoof pastern axis. Of club foot A horse with club foot has one hoof that grows more upright than the other. March 23 - Thurs.
January 27 2015 By Kentucky Equine Research Staff. Forced but limited daily exercise is essential to success. The top of the foot is usually twisted downward and inward increasing the arch and turning the heel inward.
Acquired flexural deformity club foot develops after birth. To achieve a successful outcome equine podiatry requires a team approach and. Club foot is a condition of an increased hoof angle above 60 degrees.
FIVE POTENTIAL CAUSES There are several theories on what can cause a club foot to occur. The term clubfoot gets thrown around a lot when describing the way a horse particularly a sale prospect looks.
So Called Club Foot By James R Rooney Dmv

Flexural Deformities In Horses Musculoskeletal System Merck Veterinary Manual

Ballerina Syndrome Where The Heels Remain Off The Ground Even At The Download Scientific Diagram

How D That Happen Origins And Remedies For Clubfoot Horse Racing News Paulick Report
Club Foot In Horses Equine Chronicle
Congenital Deformities Butler Professional Farrier Schools

Recognizing Various Grades Of The Club Foot Syndrome

Club Foot Or Upright Foot It S All About The Angles

The Club Foot Is It No Big Deal Or A Deal Breaker

Defining And Fixing A Horse S Club Foot

How To Treat Club Feet And Closely Related Deep Flexor Contraction